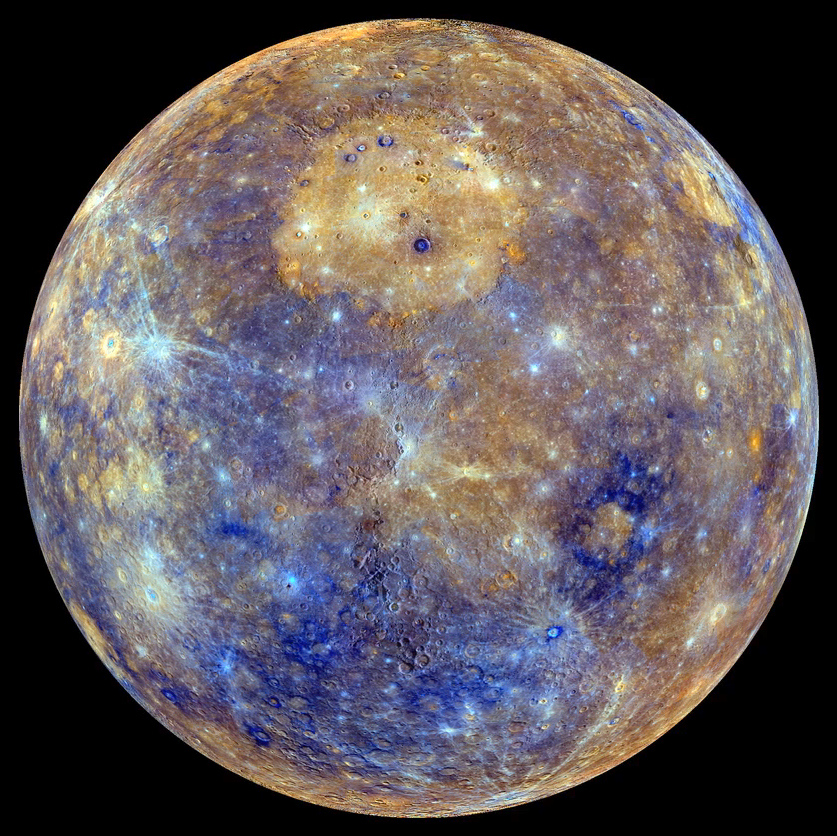
1. Mercury
Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. It is the 2nd hottest planet in the world.
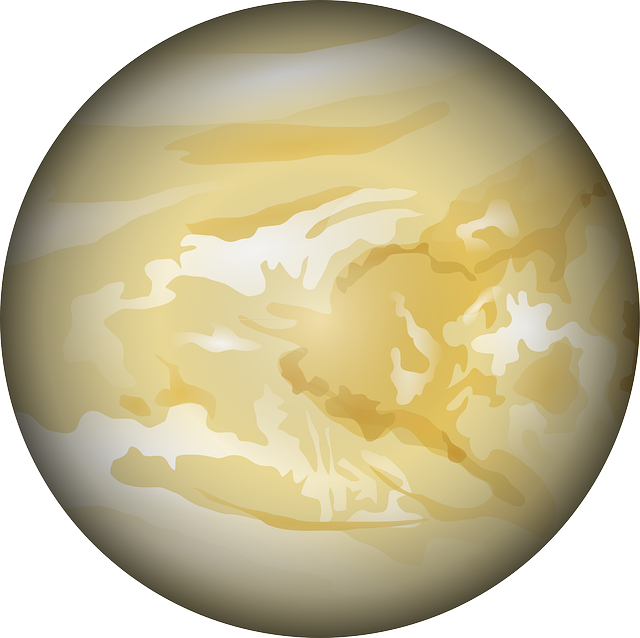

2. Venus
Venus the 2nd planet. Venus is the hottest in the world .
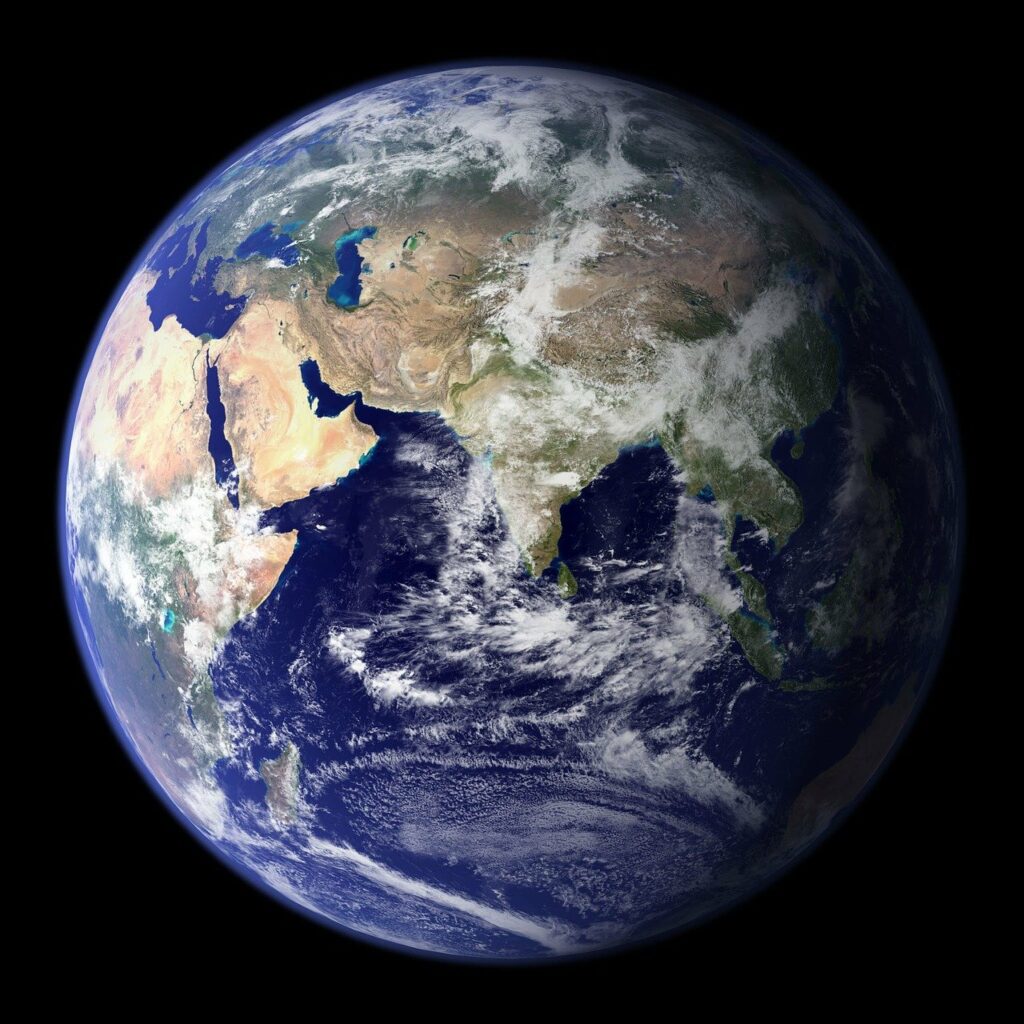

3.Earth
Earth is the third planet. it has 7 continents Aisa Africa North and South America Antartica Europe and finally Australia. There are many different animals in earth. Such like tigers, chameleons, lions, leopards and toucans. There are different people on earth some are brown[I'm brown] there are also white people.
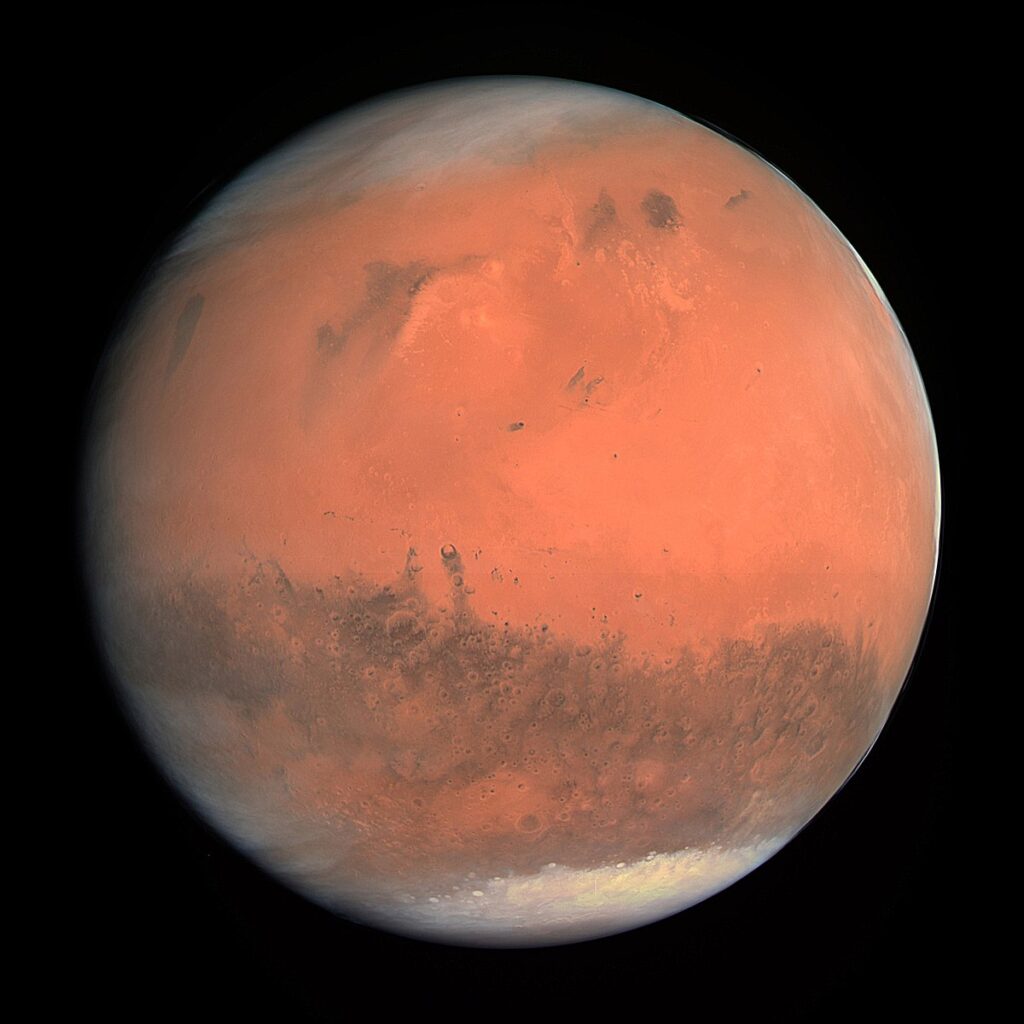

4. Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. The surface of Mars is orange-red because it is covered in iron(III) oxide dust, giving it the nickname "the Red Planet".[21][22] Mars hosts many enormous extinct volcanos (such as Olympus Mons, 21.9 km or 13.6 mi tall) and one of the largest canyons in the Solar System (Valles Marineris, 4,000 km or 2,500 mi long). For comparison, Mars's diameter is 6,779 km (4,212 mi). It is classified as a terrestrial planet and is the second smallest of the Solar System's planets.
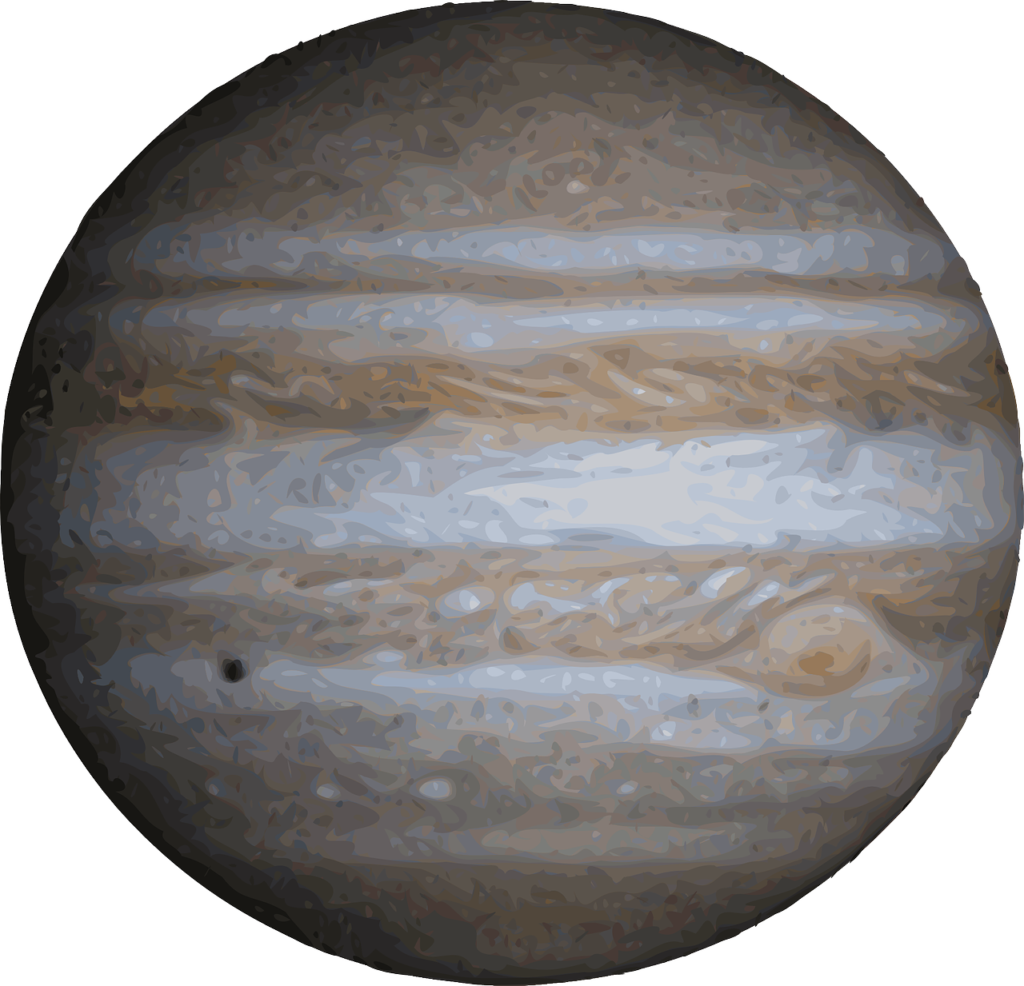

5. Jupiter
Jupiter, the fifth planet from the sun, is the largest planet in our solar system. After the Moon and Venus, it’s usually the next brightest object in the night sky. This gas giant, made mostly of hydrogen and helium, is easily recognized by its alternating dark belts and light zones as well as the Great Red Spot, a storm larger than the Earth.
6. Saturn

|
|||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈsætərn/ ⓘ[1] | ||||||||||||
|
Named after
|
Saturn | ||||||||||||
| Adjectives | Saturnian /səˈtɜːrniən/,[2] Cronian[3] / Kronian[4] /ˈkroʊniən/[5] | ||||||||||||
| Symbol | |||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
| Epoch J2000.0 | |||||||||||||
| Aphelion | 1,514.50 million km (10.1238 AU) | ||||||||||||
| Perihelion | 1,352.55 million km (9.0412 AU) | ||||||||||||
| 1,433.53 million km (9.5826 AU) | |||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.0565 | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| 378.09 days | |||||||||||||
|
Average orbital speed
|
9.68 km/s (6.01 mi/s) | ||||||||||||
| 317.020°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Inclination | |||||||||||||
| 113.665° | |||||||||||||
| 2032-Nov-29[10] | |||||||||||||
| 339.392°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Known satellites | 146 with formal designations; innumerable additional moonlets.[11][12] | ||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Mean radius
|
58,232 km (36,184 mi)[a] 9.1402 Earths |
||||||||||||
|
Equatorial radius
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Polar radius
|
|
||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0.09796 | ||||||||||||
| Circumference |
|
||||||||||||
| Volume |
|
||||||||||||
| Mass |
|
||||||||||||
|
Mean density
|
0.687 g/cm3 (0.0248 lb/cu in)[b] (less than water) 0.1246 Earths |
||||||||||||
| 0.22[15] | |||||||||||||
| 35.5 km/s (22.1 mi/s)[a] | |||||||||||||
| 10 h 32 m 36 s; 10.5433 hours,[16] 10 h 39 m; 10.7 hours[7] |
|||||||||||||
| 10h 33m 38s + 1m 52s − 1m 19s [17][18] |
|||||||||||||
|
Equatorial rotation velocity
|
9.87 km/s (6.13 mi/s; 35,500 km/h)[a] | ||||||||||||
| 26.73° (to orbit) | |||||||||||||
|
North pole right ascension
|
40.589°; 2h 42m 21s | ||||||||||||
|
North pole declination
|
83.537° | ||||||||||||
| Albedo | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| −0.55[23] to +1.17[23] | |||||||||||||
| −9.7[24] | |||||||||||||
| 14.5″ to 20.1″ (excludes rings) | |||||||||||||
| Atmosphere[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Surface pressure
|
140 kPa[25] | ||||||||||||
| 59.5 km (37.0 mi) | |||||||||||||
| Composition by volume | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine-and-a-half times that of Earth.[26][27] It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 times more massive.[28][29][30] However, even though Saturn is nearly the size of Jupiter, Saturn has less than one-third of Jupiter’s mass.
Saturn’s interior is thought to be composed of a rocky core, surrounded by a deep layer of metallicThis article is about the planet. For the deity, see Saturn (mythology). For other uses, see Saturn (disambiguation).

|
|||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈsætərn/ ⓘ[1] | ||||||||||||
|
Named after
|
Saturn | ||||||||||||
| Adjectives | Saturnian /səˈtɜːrniən/,[2] Cronian[3] / Kronian[4] /ˈkroʊniən/[5] | ||||||||||||
| Symbol | |||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
| Epoch J2000.0 | |||||||||||||
| Aphelion | 1,514.50 million km (10.1238 AU) | ||||||||||||
| Perihelion | 1,352.55 million km (9.0412 AU) | ||||||||||||
| 1,433.53 million km (9.5826 AU) | |||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.0565 | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| 378.09 days | |||||||||||||
|
Average orbital speed
|
9.68 km/s (6.01 mi/s) | ||||||||||||
| 317.020°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Inclination | |||||||||||||
| 113.665° | |||||||||||||
| 2032-Nov-29[10] | |||||||||||||
| 339.392°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Known satellites | 146 with formal designations; innumerable additional moonlets.[11][12] | ||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Mean radius
|
58,232 km (36,184 mi)[a] 9.1402 Earths |
||||||||||||
|
Equatorial radius
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Polar radius
|
|
||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0.09796 | ||||||||||||
| Circumference |
|
||||||||||||
| Volume |
|
||||||||||||
| Mass |
|
||||||||||||
|
Mean density
|
0.687 g/cm3 (0.0248 lb/cu in)[b] (less than water) 0.1246 Earths |
||||||||||||
| 0.22[15] | |||||||||||||
| 35.5 km/s (22.1 mi/s)[a] | |||||||||||||
| 10 h 32 m 36 s; 10.5433 hours,[16] 10 h 39 m; 10.7 hours[7] |
|||||||||||||
| 10h 33m 38s + 1m 52s − 1m 19s [17][18] |
|||||||||||||
|
Equatorial rotation velocity
|
9.87 km/s (6.13 mi/s; 35,500 km/h)[a] | ||||||||||||
| 26.73° (to orbit) | |||||||||||||
|
North pole right ascension
|
40.589°; 2h 42m 21s | ||||||||||||
|
North pole declination
|
83.537° | ||||||||||||
| Albedo | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| −0.55[23] to +1.17[23] | |||||||||||||
| −9.7[24] | |||||||||||||
| 14.5″ to 20.1″ (excludes rings) | |||||||||||||
| Atmosphere[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Surface pressure
|
140 kPa[25] | ||||||||||||
| 59.5 km (37.0 mi) | |||||||||||||
| Composition by volume | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine-and-a-half times that of Earth.[26][27] It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 times more massive.[28][29][30] However, even though Saturn is nearly the size of Jupiter, Saturn has less than one-third of Jupiter’s mass.
Saturn’s interior is thought to be composed of a rocky core, surrounded by a deep layer of metallicThis article is about the planet. For the deity, see Saturn (mythology). For other uses, see Saturn (disambiguation).

|
|||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈsætərn/ ⓘ[1] | ||||||||||||
|
Named after
|
Saturn | ||||||||||||
| Adjectives | Saturnian /səˈtɜːrniən/,[2] Cronian[3] / Kronian[4] /ˈkroʊniən/[5] | ||||||||||||
| Symbol | |||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
| Epoch J2000.0 | |||||||||||||
| Aphelion | 1,514.50 million km (10.1238 AU) | ||||||||||||
| Perihelion | 1,352.55 million km (9.0412 AU) | ||||||||||||
| 1,433.53 million km (9.5826 AU) | |||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.0565 | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| 378.09 days | |||||||||||||
|
Average orbital speed
|
9.68 km/s (6.01 mi/s) | ||||||||||||
| 317.020°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Inclination | |||||||||||||
| 113.665° | |||||||||||||
| 2032-Nov-29[10] | |||||||||||||
| 339.392°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Known satellites | 146 with formal designations; innumerable additional moonlets.[11][12] | ||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Mean radius
|
58,232 km (36,184 mi)[a] 9.1402 Earths |
||||||||||||
|
Equatorial radius
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Polar radius
|
|
||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0.09796 | ||||||||||||
| Circumference |
|
||||||||||||
| Volume |
|
||||||||||||
| Mass |
|
||||||||||||
|
Mean density
|
0.687 g/cm3 (0.0248 lb/cu in)[b] (less than water) 0.1246 Earths |
||||||||||||
| 0.22[15] | |||||||||||||
| 35.5 km/s (22.1 mi/s)[a] | |||||||||||||
| 10 h 32 m 36 s; 10.5433 hours,[16] 10 h 39 m; 10.7 hours[7] |
|||||||||||||
| 10h 33m 38s + 1m 52s − 1m 19s [17][18] |
|||||||||||||
|
Equatorial rotation velocity
|
9.87 km/s (6.13 mi/s; 35,500 km/h)[a] | ||||||||||||
| 26.73° (to orbit) | |||||||||||||
|
North pole right ascension
|
40.589°; 2h 42m 21s | ||||||||||||
|
North pole declination
|
83.537° | ||||||||||||
| Albedo | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| −0.55[23] to +1.17[23] | |||||||||||||
| −9.7[24] | |||||||||||||
| 14.5″ to 20.1″ (excludes rings) | |||||||||||||
| Atmosphere[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Surface pressure
|
140 kPa[25] | ||||||||||||
| 59.5 km (37.0 mi) | |||||||||||||
| Composition by volume | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine-and-a-half times that of Earth.[26][27] It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 times more massive.[28][29][30] However, even though Saturn is nearly the size of Jupiter, Saturn has less than one-third of Jupiter’s mass.
Saturn’s interior is thought to be composed of a rocky core, surrounded by a deep layer of metallicThis article is about the planet. For the deity, see Saturn (mythology). For other uses, see Saturn (disambiguation).

|
|||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈsætərn/ ⓘ[1] | ||||||||||||
|
Named after
|
Saturn | ||||||||||||
| Adjectives | Saturnian /səˈtɜːrniən/,[2] Cronian[3] / Kronian[4] /ˈkroʊniən/[5] | ||||||||||||
| Symbol | |||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
| Epoch J2000.0 | |||||||||||||
| Aphelion | 1,514.50 million km (10.1238 AU) | ||||||||||||
| Perihelion | 1,352.55 million km (9.0412 AU) | ||||||||||||
| 1,433.53 million km (9.5826 AU) | |||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.0565 | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| 378.09 days | |||||||||||||
|
Average orbital speed
|
9.68 km/s (6.01 mi/s) | ||||||||||||
| 317.020°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Inclination | |||||||||||||
| 113.665° | |||||||||||||
| 2032-Nov-29[10] | |||||||||||||
| 339.392°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Known satellites | 146 with formal designations; innumerable additional moonlets.[11][12] | ||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Mean radius
|
58,232 km (36,184 mi)[a] 9.1402 Earths |
||||||||||||
|
Equatorial radius
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Polar radius
|
|
||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0.09796 | ||||||||||||
| Circumference |
|
||||||||||||
| Volume |
|
||||||||||||
| Mass |
|
||||||||||||
|
Mean density
|
0.687 g/cm3 (0.0248 lb/cu in)[b] (less than water) 0.1246 Earths |
||||||||||||
| 0.22[15] | |||||||||||||
| 35.5 km/s (22.1 mi/s)[a] | |||||||||||||
| 10 h 32 m 36 s; 10.5433 hours,[16] 10 h 39 m; 10.7 hours[7] |
|||||||||||||
| 10h 33m 38s + 1m 52s − 1m 19s [17][18] |
|||||||||||||
|
Equatorial rotation velocity
|
9.87 km/s (6.13 mi/s; 35,500 km/h)[a] | ||||||||||||
| 26.73° (to orbit) | |||||||||||||
|
North pole right ascension
|
40.589°; 2h 42m 21s | ||||||||||||
|
North pole declination
|
83.537° | ||||||||||||
| Albedo | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| −0.55[23] to +1.17[23] | |||||||||||||
| −9.7[24] | |||||||||||||
| 14.5″ to 20.1″ (excludes rings) | |||||||||||||
| Atmosphere[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Surface pressure
|
140 kPa[25] | ||||||||||||
| 59.5 km (37.0 mi) | |||||||||||||
| Composition by volume | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine-and-a-half times that of Earth.[26][27] It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 times more massive.[28][29][30] However, even though Saturn is nearly the size of Jupiter, Saturn has less than one-third of Jupiter’s mass.
Saturn’s interior is thought to be composed of a rocky core, surrounded by a deep layer of metallicThis article is about the planet. For the deity, see Saturn (mythology). For other uses, see Saturn (disambiguation).

|
|||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈsætərn/ ⓘ[1] | ||||||||||||
|
Named after
|
Saturn | ||||||||||||
| Adjectives | Saturnian /səˈtɜːrniən/,[2] Cronian[3] / Kronian[4] /ˈkroʊniən/[5] | ||||||||||||
| Symbol | |||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
| Epoch J2000.0 | |||||||||||||
| Aphelion | 1,514.50 million km (10.1238 AU) | ||||||||||||
| Perihelion | 1,352.55 million km (9.0412 AU) | ||||||||||||
| 1,433.53 million km (9.5826 AU) | |||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.0565 | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| 378.09 days | |||||||||||||
|
Average orbital speed
|
9.68 km/s (6.01 mi/s) | ||||||||||||
| 317.020°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Inclination | |||||||||||||
| 113.665° | |||||||||||||
| 2032-Nov-29[10] | |||||||||||||
| 339.392°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Known satellites | 146 with formal designations; innumerable additional moonlets.[11][12] | ||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Mean radius
|
58,232 km (36,184 mi)[a] 9.1402 Earths |
||||||||||||
|
Equatorial radius
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Polar radius
|
|
||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0.09796 | ||||||||||||
| Circumference |
|
||||||||||||
| Volume |
|
||||||||||||
| Mass |
|
||||||||||||
|
Mean density
|
0.687 g/cm3 (0.0248 lb/cu in)[b] (less than water) 0.1246 Earths |
||||||||||||
| 0.22[15] | |||||||||||||
| 35.5 km/s (22.1 mi/s)[a] | |||||||||||||
| 10 h 32 m 36 s; 10.5433 hours,[16] 10 h 39 m; 10.7 hours[7] |
|||||||||||||
| 10h 33m 38s + 1m 52s − 1m 19s [17][18] |
|||||||||||||
|
Equatorial rotation velocity
|
9.87 km/s (6.13 mi/s; 35,500 km/h)[a] | ||||||||||||
| 26.73° (to orbit) | |||||||||||||
|
North pole right ascension
|
40.589°; 2h 42m 21s | ||||||||||||
|
North pole declination
|
83.537° | ||||||||||||
| Albedo | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| −0.55[23] to +1.17[23] | |||||||||||||
| −9.7[24] | |||||||||||||
| 14.5″ to 20.1″ (excludes rings) | |||||||||||||
| Atmosphere[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Surface pressure
|
140 kPa[25] | ||||||||||||
| 59.5 km (37.0 mi) | |||||||||||||
| Composition by volume | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine-and-a-half times that of Earth.[26][27] It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 times more massive.[28][29][30] However, even though Saturn is nearly the size of Jupiter, Saturn has less than one-third of Jupiter’s mass.
Saturn’s interior is thought to be composed of a rocky core, surrounded by a deep layer of metallicThis article is about the planet. For the deity, see Saturn (mythology). For other uses, see Saturn (disambiguation).

|
|||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈsætərn/ ⓘ[1] | ||||||||||||
|
Named after
|
Saturn | ||||||||||||
| Adjectives | Saturnian /səˈtɜːrniən/,[2] Cronian[3] / Kronian[4] /ˈkroʊniən/[5] | ||||||||||||
| Symbol | |||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
| Epoch J2000.0 | |||||||||||||
| Aphelion | 1,514.50 million km (10.1238 AU) | ||||||||||||
| Perihelion | 1,352.55 million km (9.0412 AU) | ||||||||||||
| 1,433.53 million km (9.5826 AU) | |||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.0565 | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| 378.09 days | |||||||||||||
|
Average orbital speed
|
9.68 km/s (6.01 mi/s) | ||||||||||||
| 317.020°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Inclination | |||||||||||||
| 113.665° | |||||||||||||
| 2032-Nov-29[10] | |||||||||||||
| 339.392°[8] | |||||||||||||
| Known satellites | 146 with formal designations; innumerable additional moonlets.[11][12] | ||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Mean radius
|
58,232 km (36,184 mi)[a] 9.1402 Earths |
||||||||||||
|
Equatorial radius
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Polar radius
|
|
||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0.09796 | ||||||||||||
| Circumference |
|
||||||||||||
| Volume |
|
||||||||||||
| Mass |
|
||||||||||||
|
Mean density
|
0.687 g/cm3 (0.0248 lb/cu in)[b] (less than water) 0.1246 Earths |
||||||||||||
| 0.22[15] | |||||||||||||
| 35.5 km/s (22.1 mi/s)[a] | |||||||||||||
| 10 h 32 m 36 s; 10.5433 hours,[16] 10 h 39 m; 10.7 hours[7] |
|||||||||||||
| 10h 33m 38s + 1m 52s − 1m 19s [17][18] |
|||||||||||||
|
Equatorial rotation velocity
|
9.87 km/s (6.13 mi/s; 35,500 km/h)[a] | ||||||||||||
| 26.73° (to orbit) | |||||||||||||
|
North pole right ascension
|
40.589°; 2h 42m 21s | ||||||||||||
|
North pole declination
|
83.537° | ||||||||||||
| Albedo | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| −0.55[23] to +1.17[23] | |||||||||||||
| −9.7[24] | |||||||||||||
| 14.5″ to 20.1″ (excludes rings) | |||||||||||||
| Atmosphere[6] | |||||||||||||
|
Surface pressure
|
140 kPa[25] | ||||||||||||
| 59.5 km (37.0 mi) | |||||||||||||
| Composition by volume | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine-and-a-half times that of Earth.[26][27] It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 times more massive.[28][29][30] However, even though Saturn is nearly the size of Jupiter, Saturn has less than one-third of Jupiter’s mass.
Saturn’s interior is thought to be composed of a rocky core, surrounded by a deep layer of metallic

7. Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the sun. It has the third-largest radius of all the planets. It has 13 faint rings and 27 small moons. But a characteristic that sets Uranus apart: It spins on its side as it orbits the sun. That trip takes about 84 Earth years.
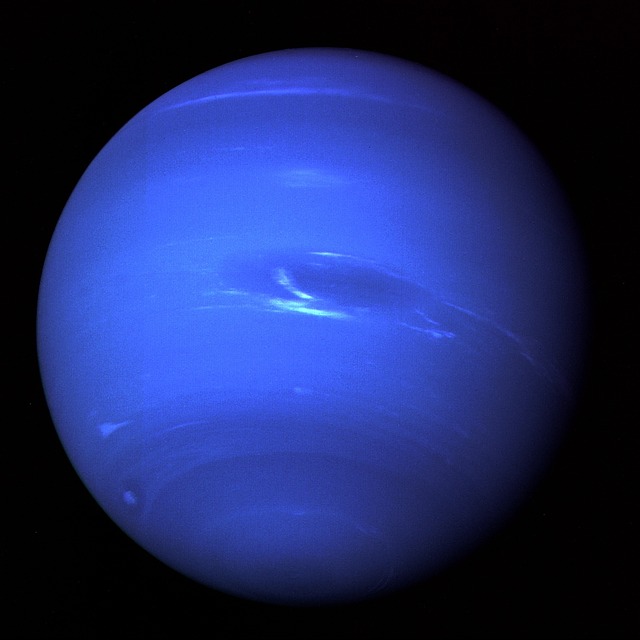

8. Neptune
Neptune
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NeptuneNeptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than fellow ice giant Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more grSee more
Discovery date23 September 1846Named afterLatin Neptunus, via French NeptuneAdjectivesNeptunian (/nɛpˈtjuːniən/), PoseideanHistorySome of the earliest recorded observations ever made through a telescope, Galileo Galilei‘s drawings on 28 December 1612 and 27 January 1613 contain plotted points that match with what is now known to have been the po… See more
Physical characteristicsNeptune’s mass of 1.0243×10 kg is intermediate between Earth and the larger gas giants: it is 17 times that of Earth but just 1/19th that of Jupiter. Its gravity at 1 bar is 11.15 m/s , 1.14 times the surface gravity of Earth, an… See more
ClimateNeptune’s weather is characterised by extremely dynamic storm systems, with winds reaching speeds of almost 600 m/s (2,200 km/h; 1,300 mph)—exceeding supersonic flow. More typically, by tracking the motion o… See more
ContentHistoryPhysical characteristicsClimateNeptune – Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NeptuneNeptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than fellow ice giant Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more grSee more
Discovery date23 September 1846Named afterLatin Neptunus, via French NeptuneAdjectivesNeptunian (/nɛpˈtjuːniən/), PoseideanHistorySome of the earliest recorded observations ever made through a telescope, Galileo Galilei‘s drawings on 28 December 1612 and 27 January 1613 contain plotted points that match with what is now known to have been the po… See more
Physical characteristicsNeptune’s mass of 1.0243×10 kg is intermediate between Earth and the larger gas giants: it is 17 times that of Earth but just 1/19th that of Jupiter. Its gravity at 1 bar is 11.15 m/s , 1.14 times the surface gravity of Earth, an… See more
ClimateNeptune’s weather is characterised by extremely dynamic storm systems, with winds reaching speeds of almost 600 m/s (2,200 km/h; 1,300 mph)—exceeding supersonic flow. More typically, by tracking the motion o… See more
WebDark, cold and whipped by supersonic winds, giant Neptune is the eighth and most distant major planet orbiting our Sun. More than 30 times as far from the Sun as Earth, Neptune …
News about Neptune
bing.com/newsExplore More News
Web5 days ago · Neptune, third most massive planet in the solar system and the eighth and outermost planet from the Sun. Neptune has 14 moons, only two of which were discovered before Voyager 2’s visit in 1989, and a system …
WebJan 25, 2024 · Learn about Neptune, the last of the planets in our solar system, and its six rings, 14 moons, and windy atmosphere. Explore Neptune’s structure, surface, history, and features with 3D models and …
- See More
- OVERVIEW
- COMPARE
- QUIZ
Explore in the solar systemNeptune, the eighth planet from the sun, is the fourth largest planet in the solar system, but because it is so far away, it is not visible to the naked eye. Images from Voyager 1 show a vibrant blue Neptune with 14 moons, including its largest moon, Triton, discovered just 17 days after Neptune was first documented in 1846.Radius:15,299.4 milesType:ice giantEffective temperature:-353.2°FGravity:36.58 feet/s²Data from: NASA WebLearn about Neptune, the outermost planet in our solar system, from its atmosphere to its moons to its rings. Find out how Voyager 2 visited Neptune, what we discovered, and what we still need to know.
- Results near West Bromwich, West Midlands · Based on device location ·
Hotels | Neptune, NJ
https://www.bing.com/travel/hotelsHoliday Inn Express Neptune, an IHG Hotel
2-star hotel · NeptuneTripadvisor (378)DEAL-11%$136$153Hampton Inn Neptune/Wall
3-star hotel · NeptuneTripadvisor (830)$195Residence Inn by Marriott Neptune at G…
3-star hotel · NeptuneTripadvisor (282)$169See more hotels WebSep 25, 2019 · Learn about Neptune, the fourth largest and the farthest planet of the Solar System, discovered by mathematical predictions in 1846. Find out its key facts, such as its color, wind speed, rings, satellites, and …
Related searches for neptune
Neptune Eighth planet from the Sun Size Atmosphere Discovery Exploration Moons Mythology Facts Images Neptune – Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neptune Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than fellow ice giant Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gr– Wikipedia
WebDark, cold and whipped by supersonic winds, giant Neptune is the eighth and most distant major planet orbiting our Sun. More than 30 times as far from the Sun as Earth, Neptune …
News about Neptune
bing.com/newsExplore More News
Web5 days ago · Neptune, third most massive planet in the solar system and the eighth and outermost planet from the Sun. Neptune has 14 moons, only two of which were discovered before Voyager 2’s visit in 1989, and a system …
WebJan 25, 2024 · Learn about Neptune, the last of the planets in our solar system, and its six rings, 14 moons, and windy atmosphere. Explore Neptune’s structure, surface, history, and features with 3D models and …
- See More
- OVERVIEW
- COMPARE
- QUIZ
Explore in the solar systemNeptune, the eighth planet from the sun, is the fourth largest planet in the solar system, but because it is so far away, it is not visible to the naked eye. Images from Voyager 1 show a vibrant blue Neptune with 14 moons, including its largest moon, Triton, discovered just 17 days after Neptune was first documented in 1846.Radius:15,299.4 milesType:ice giantEffective temperature:-353.2°FGravity:36.58 feet/s²Data from: NASA WebLearn about Neptune, the outermost planet in our solar system, from its atmosphere to its moons to its rings. Find out how Voyager 2 visited Neptune, what we discovered, and what we still need to know.
- Results near West Bromwich, West Midlands · Based on device location ·
Hotels | Neptune, NJ
https://www.bing.com/travel/hotelsHoliday Inn Express Neptune, an IHG Hotel
2-star hotel · NeptuneTripadvisor (378)DEAL-11%$136$153Hampton Inn Neptune/Wall
3-star hotel · NeptuneTripadvisor (830)$195Residence Inn by Marriott Neptune at G…
3-star hotel · NeptuneTripadvisor (282)$169See more hotels WebSep 25, 2019 · Learn about Neptune, the fourth largest and the farthest planet of the Solar System, discovered by mathematical predictions in 1846. Find out its key facts, such as its color, wind speed, rings, satellites, and …
Related searches for neptune







